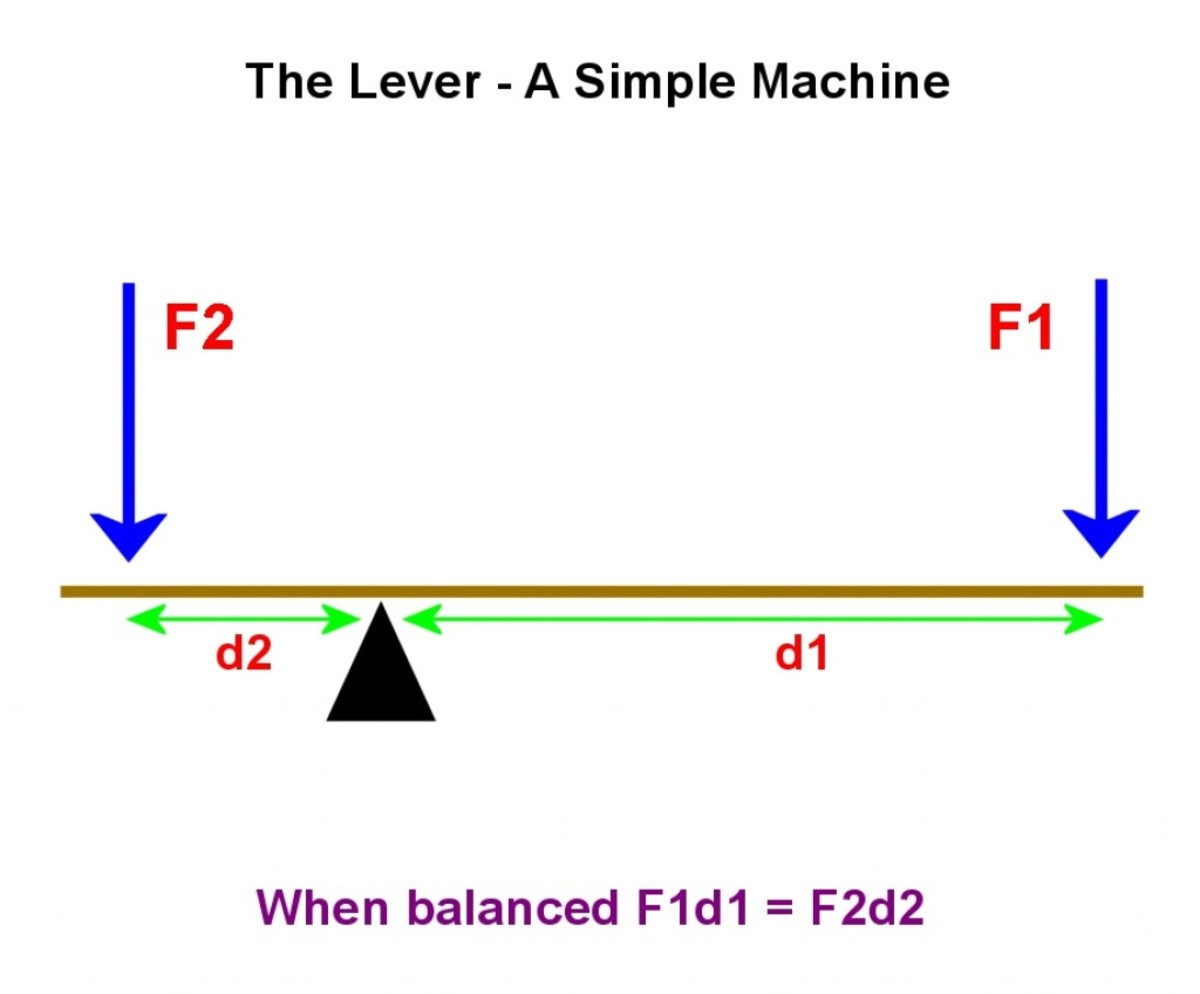
How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces . levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. They both take advantage of forces and moments. As the small wheel turns, the rotational effect is transmitted to the larger wheel. Where the gears meet, the teeth must. revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. When using gears, we exert force (effort) on the smaller wheel (load). Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. rotation and transmission of forces by gears. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. Levers are capable of taking an. the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it.
from owlcation.com
Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. They both take advantage of forces and moments. the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it.
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation
How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces rotation and transmission of forces by gears. the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. When using gears, we exert force (effort) on the smaller wheel (load). Where the gears meet, the teeth must. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. Levers are capable of taking an. rotation and transmission of forces by gears. This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. As the small wheel turns, the rotational effect is transmitted to the larger wheel. They both take advantage of forces and moments.
From www.youtube.com
Levers as Force Multipliers and Gears GCSE Physics Revision YouTube How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. As the small wheel turns, the rotational effect is transmitted to the larger wheel. When using gears, we exert force (effort) on the smaller wheel (load). the opposite end is also. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.physicsforums.com
Understanding Torque The Basics and How It Relates to Rotational Force How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. Levers are capable of taking an. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.youtube.com
How Levers, Pulleys and Gears Work YouTube How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. Where the gears meet, the teeth. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.youtube.com
Mechanical Video 2 Lever Calculations YouTube How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces rotation and transmission of forces by gears. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. As the small wheel turns, the rotational effect is transmitted to the larger wheel. When using gears, we exert force (effort) on the smaller wheel (load). the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. Where the. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From school.careers360.com
types of lever Overview, Structure, Properties & Uses How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces rotation and transmission of forces by gears. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. Where the gears meet, the teeth must. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. They both take advantage of forces and moments. Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. As. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From slidetodoc.com
Chapter 8 Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamics Force How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. Moment = force × distance. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From chemistrylabs-2.blogspot.com
Lever Arm Principle Chemistry Labs How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. As the small wheel turns, the rotational effect is transmitted to the larger wheel. This has the effect of rotating or lifting. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From exodhwybi.blob.core.windows.net
How Does A Sailboat Use A Pulley System at Tony Flores blog How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. Levers are capable of taking an. Moment = force × distance (m = fd) levers. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. If an object. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From physics.stackexchange.com
rotational dynamics Lever armdefinition Physics Stack Exchange How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. If an object is in equilibrium,. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.researchgate.net
Direction of thrust and rotational forces in a spiral bevel gear Download Scientific Diagram How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces Levers are capable of taking an. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. rotation and transmission of. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces If an object is in equilibrium, there is no resultant force or moment on it. by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. rotation and transmission of forces by gears. a force can produce a turning effect known. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. Where the gears meet, the teeth must. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. a force can produce a turning effect known as a moment. Moment. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.teachit.co.uk
Levers, moments and gears KS4 PPT lesson Teachit How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn.. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From schematicficklesicko3v.z14.web.core.windows.net
Diagrams To Set Up Pulleys How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces rotation and transmission of forces by gears. the opposite end is also rotated about the pivot in the same direction. Where the gears meet, the teeth must. revision notes on 5.4.3 levers & gears for the aqa gcse physics syllabus, written by the physics experts at save my exams. by the end of this lesson, you. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From owlcation.com
Simple Machines How Does a Lever Work? Owlcation How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. Levers are capable of taking an. They both take advantage of forces and moments. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. As one gear turns, the other gear. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From byjus.com
How do levers work? How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces This has the effect of rotating or lifting the load. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. Levers are capable of taking an. Where the gears meet, the teeth must. As one gear turns, the other gear must also turn. a force can produce a turning effect known as. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From kinesiologykris.com
The 3 Classes of Levers How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces When using gears, we exert force (effort) on the smaller wheel (load). rotation and transmission of forces by gears. They both take advantage of forces and moments. Similar to a lever, gears also transmit turning effects and they are used to multiply a force. levers and gears are mechanical components which transmit rotational motion. the opposite end. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.
From www.pinterest.com
Cub Scouts Learn About Levers for Swing! Nova Award Science education, Human body worksheets How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces by the end of this lesson, you are going to be able to describe how forces cause objects to turn by producing a rotational effect called a. rotation and transmission of forces by gears. Levers are capable of taking an. They both take advantage of forces and moments. a force can produce a turning effect known as. How Levers And Gears Transmit The Rotational Effects Of Forces.